Extraction Engines Available to MICO
The primary goal of MICO is to build on existing extraction technologies and improve them so they can be used in cooperation instead of developing completely new extraction approaches. To ensure we have a sufficient diversity in cross-media extraction technologies right at the start of the project, several partners bring in technologies they have developed or they have been working with.
The following table summarises the extraction technologies available to MICO. Some functionalities might be covered by different tools with different quality characteristics. For each tool we give the partner who has expertise and the license. Note that there are considerable differences in Open Source licenses: whereas the Apache and BSD licenses are very liberal regarding commercial use, the GPL typically precludes this kind of exploitation.
Orchestrating Extractors
MICO Pipelines are a combination of extractors in a graph like structure to be executed in a specific order to produce cross-media annotations. In order to have a first system ready by the start of the project we implemented a simple orchestration approach in our first MICO broker version. It used a simple mime type-based connections (i.e. string comparison) approach to register extractor processes, determine their dependencies, and to automatically configure pipelines based on these dependencies. However, this meant that all possible connections between all registered extractor processes were established, including unintended connections or even connections producing loops. Therefore, the approach had to be improved in order to support the following features:
- Standardized way of parameter specification passed to the extractor during start-up
- Means of pipeline configuration defining the extractors involved and their parameters
- End-User controlled start-up and shut-down of extractors establishing a pipeline for a specific purposes
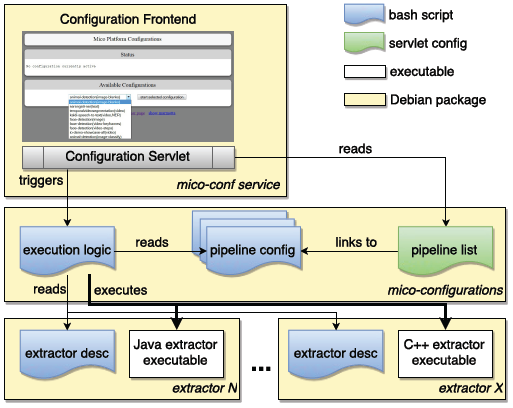
We opted for an approach using a mixture of bash scripts and servlet configurations which is shown in the figure below. Every extractor deployed for the MICO system is obliged to support standard start-up and shut-down command line parameters. It also needs to be packaged with a short description bash script specifying the name, description and system (native, Java) it is running for. For easy changes and updates, the pipelines are configured in a separate Debian package. They specify the extractors to be loaded and the parameters to be passed in addition to the run/stop arguments.
With the release of the final broker version 3 this system is not used anymore for creating MICO processing routes but rather serves as a simple run time configuration system that is now just responsible for starting and shutting down the extractors that might belong to different routes (via the broker web front end). It’s not required to be used though and could be replaced by a different distributed run time management system at any time. In the ideal case of a large scale distribute system, several instance of each extractor in each mode would just be run and execution order selection is completely carried out by the broker.
Details about the broker are given in the broker section .